Drag Force
A drag force is the resistance force caused by the motion of a body through a fluid, such as water or air. A drag force acts opposite to the direction of the oncoming flow velocity. This is the relative velocity between the body and the fluid.The drag force D exerted on a body traveling though a fluid is given by
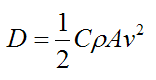
Where:
C is the drag coefficient, which can vary along with the speed of the body. But typical values range from 0.4 to 1.0 for different fluids (such as air and water)
ρ is the density of the fluid through which the body is moving
v is the speed of the body relative to the fluid
A is the projected cross-sectional area of the body perpendicular to the flow direction (that is, perpendicular to v). This is illustrated in the figure below
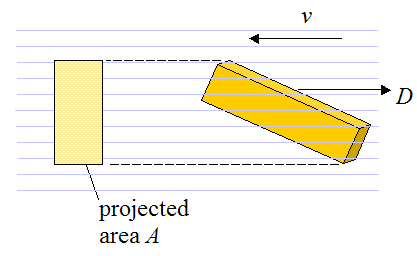
To see an example of a problem that involves drag, go to The physics of skydiving.
Return to Dynamics page
Return to Real World Physics Problems home page
Free Newsletter
Subscribe to my free newsletter below. In it I explore physics ideas that seem like science fiction but could become reality in the distant future. I develop these ideas with the help of AI. I will send it out a few times a month.